The article has been reviewed by ENT Specialist in Otorhinolaryngology, Dr. Lau Kai Yum, Jonathan.

The tonsils are part of the human immune system; however, they are also prone to infections by viruses or bacteria, leading to tonsillitis. Tonsillitis can cause discomfort such as sore throat and difficulty in swallowing, and it may also trigger other health issues. Therefore, it is crucial to learn more and understand the symptoms, causes, and treatment methods for tonsillitis.
What is Tonsillitis?
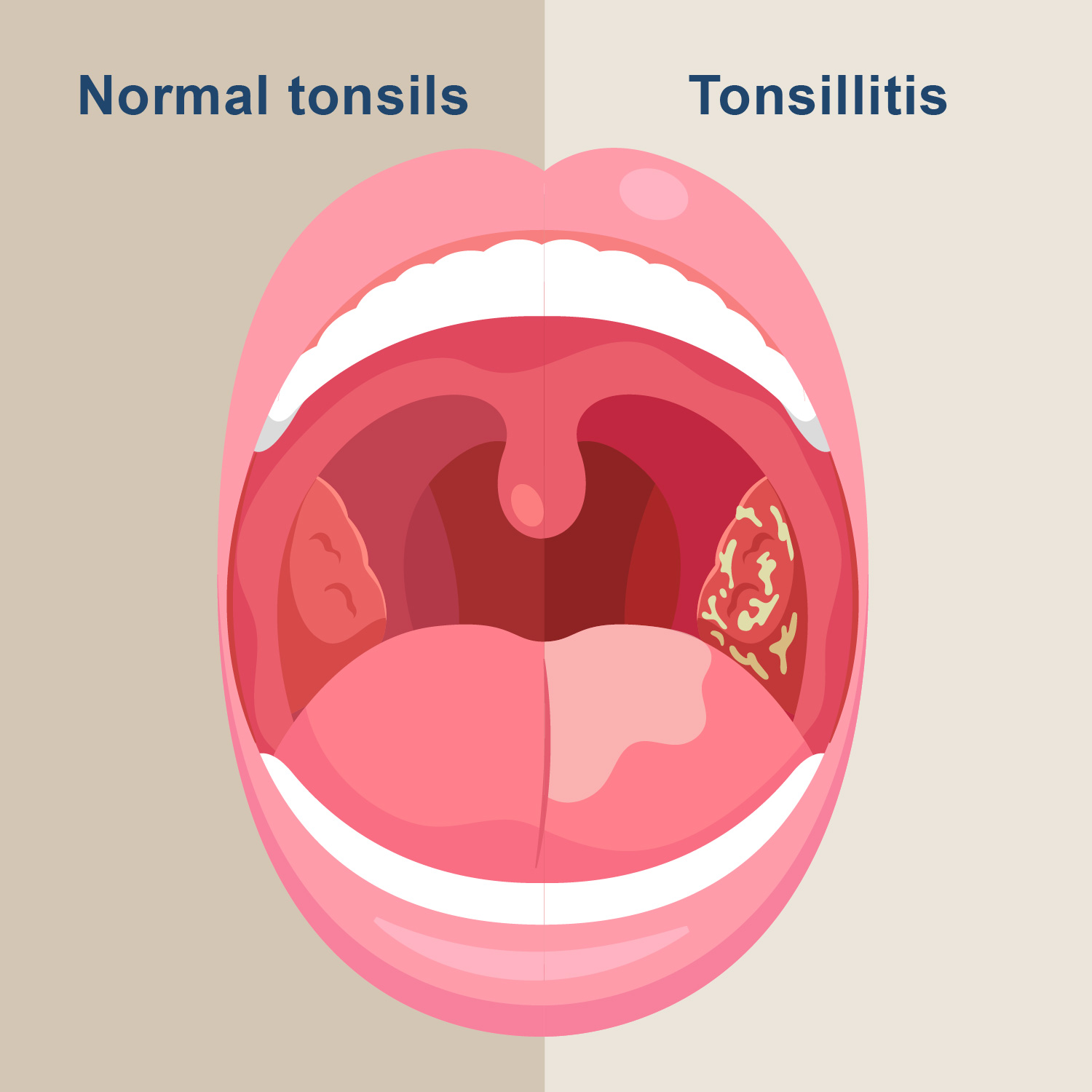
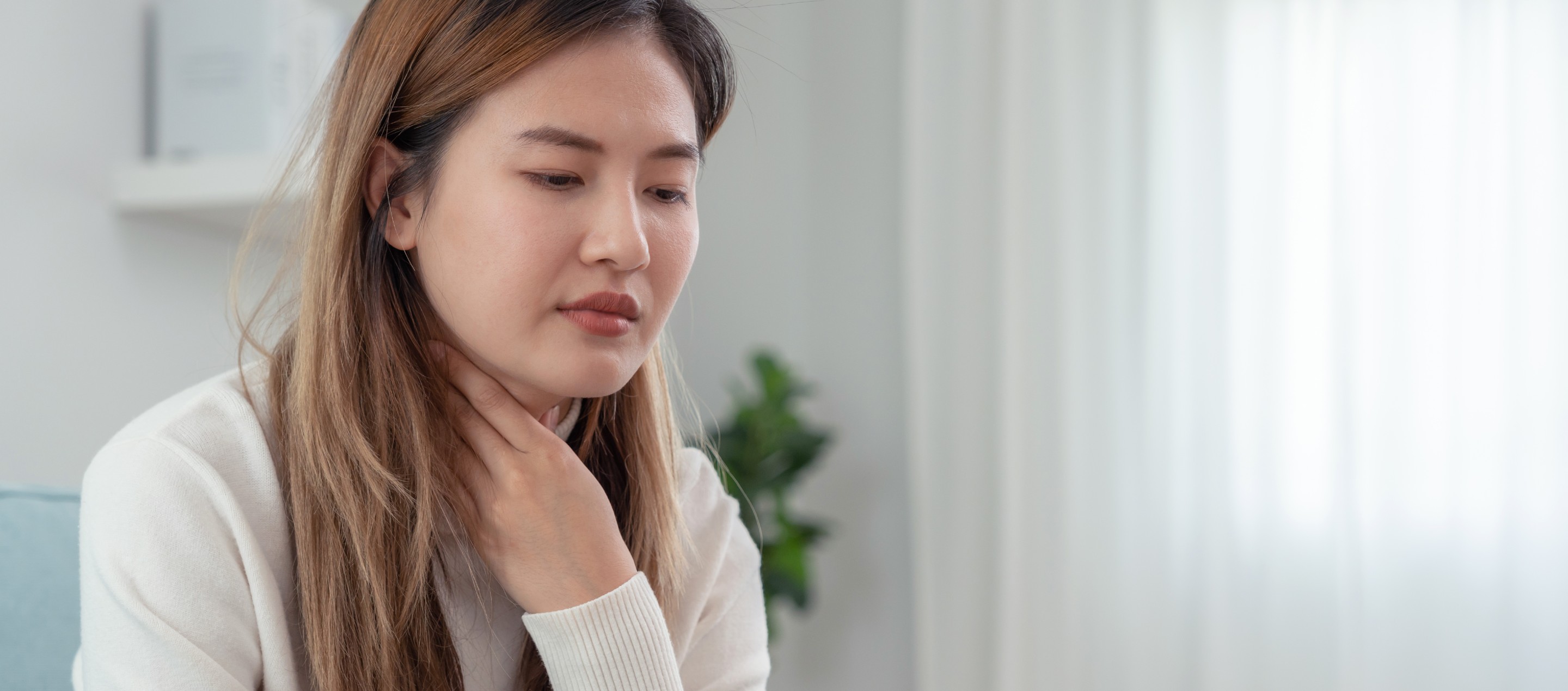
The palatine tonsils are structures of lymphatic tissue on both sides of the throat, above and behind the tongue. The tonsils play a vital role in the immune system which helps the body fight infection. Normal tonsils help the body combat foreign pathogens by producing antibodies. However, the surface of the tonsils has irregular crypts or small pits, and this structure makes it easy for bacteria to thrive. If pathogens proliferate in large numbers, it can lead to tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis is mainly divided into the following three categories:
Acute tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis is usually associated with upper respiratory infections, with common pathogens being viruses or bacteria. The main symptoms for patients include sore throat, difficulty in swallowing, fever, and cough etc, with the condition generally lasting from three days to two weeks.
Recurrent tonsillitis
Recurrent tonsillitis refers to the recurring occurrence of tonsillitis, significantly affecting the patient's quality of life. Some patients may experience episodes once a month, with each episode lasting up to two weeks, causing disruptions in their daily life and work.
Chronic tonsillitis
The symptoms of chronic tonsillitis are usually milder than those of acute inflammation but this intermittent symptoms persist over time. Patients may experience throat’s discomfort , such as a sensation of a foreign body or slight pain, for three months or over a year. Chronic inflammation may also lead to the enlargement of tonsillar crypts, making it easier for food debris to accumulate, which can form tonsil stones and cause issues like bad breath.
Causes of tonsillitis
Bacterial infection
Tonsillitis caused by bacteria (especially streptococcus) is also known as streptococcal pharyngitis or throat infection. This type of infection is highly contagious and requires timely treatment to avoid severe complications.
Viral infection
Several viruses, including adenovirus, rhinovirus, influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and enteroviruses, can also lead to tonsillitis.
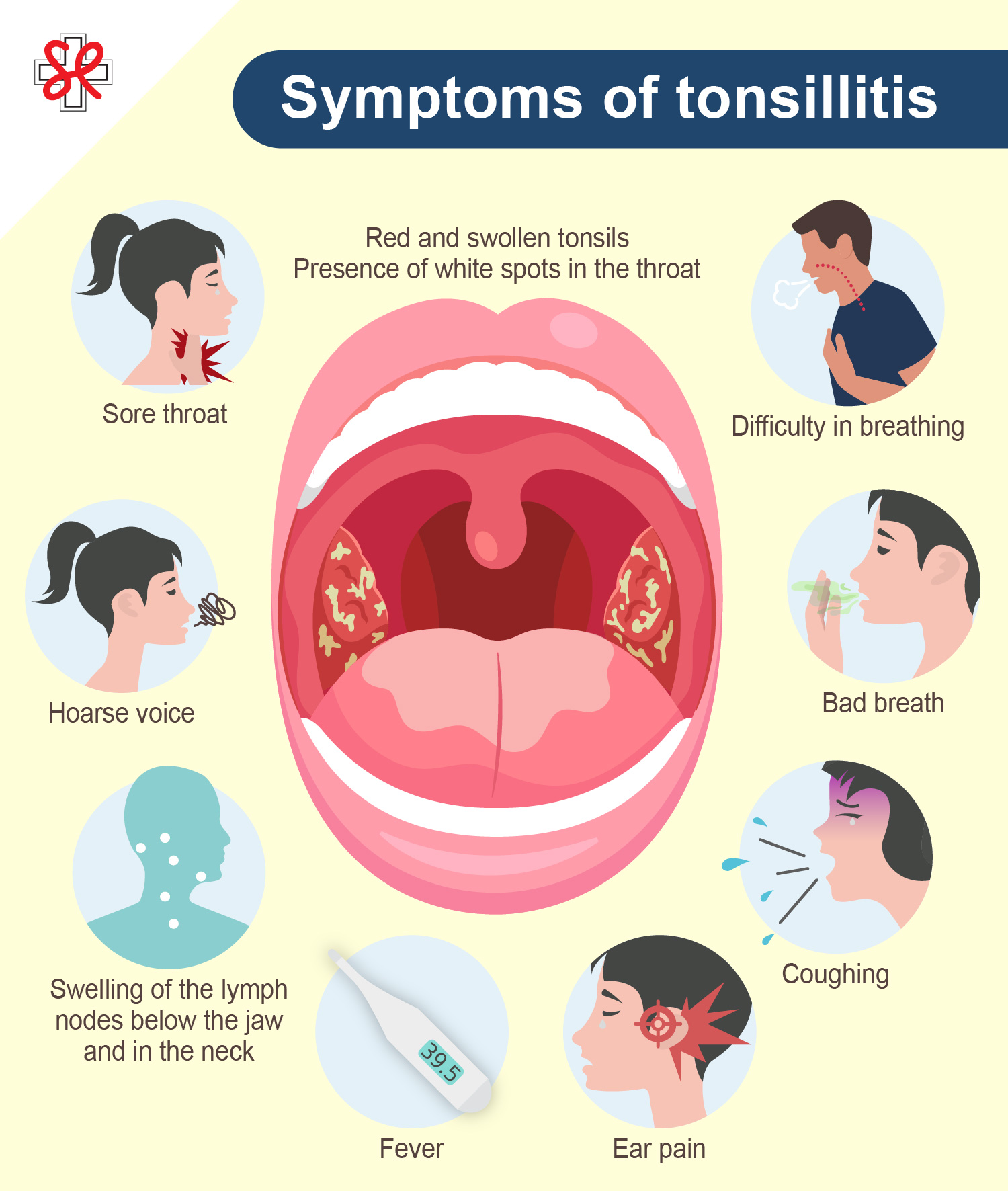
Symptoms of tonsillitis
( ![]() Click the image to enlarge )
Click the image to enlarge )
- Red and swollen tonsils
- Presence of white spots in the throat
- Sore throat
- Hoarse voice
- Swelling of the lymph nodes below the jaw and in the neck
- Fever
- Ear pain
- Coughing
- Bad breath
- Difficulty in breathing
How is tonsillitis diagnosed?
Symptom assessment
The doctor will carefully inquire about the patient's symptoms, including: the severity and duration of sore throat, whether there is difficulty or pain when swallowing, whether there are other symptoms such as fever, cough, or nasal congestion, any past history of tonsillitis, and if there has been contact with others who have similar symptoms.
Throat examination
The doctor will use a tongue depressor to observe the patient's throat and examine the condition of the tonsils. If red and swollen tonsils are found, along with white or yellow spots and pus on the surface of the tonsils, or redness and swelling on the posterior wall of the throat, this may indicate tonsillitis.
Bacterial culture
The doctor will use a cotton swab to gently scrape the secretions at the back of your throat and then send it to the pathology laboratory for a bacterial culture to identify the pathogens. This method can more accurately identify the type of bacteria causing the infection and the doctor can then prescribe appropriate antibiotics for treatment.
Blood Test
A blood test, known as complete blood cell count (CBC), is a common examination that measures the number and type of cells in your blood. This test can help the doctor preliminarily evaluate the cause and severity of the infection, which aids in devising an appropriate treatment plan.
How is tonsillitis treated?
There are many ways to treat tonsillitis, and the doctor will determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment methods:
Antibiotics
If tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection and there is an occurrence of pus, the doctor will recommend treating it with antibiotics. For most early or milder cases of infection, doctors will prescribe oral antibiotics for outpatient treatment. However, some patients with severe conditions or those who cannot tolerate oral medication will need to be hospitalized. During hospitalization, healthcare providers will administer antibiotics via intravenous injection to ensure that the medication quickly and effectively enters the patient's bloodstream for better treatment outcomes.
Surgery
If a patient suffers from recurrent or chronic tonsillitis, the doctor may recommend a tonsillectomy to reduce the risk of complications arising from inflammation. Depending on the patient's condition, the doctor may use advanced tonsillectomy device to precisely remove the tonsil tissue while effectively minimizing thermal damage to surrounding tissues, which helps relieve postoperative pain.
Although tonsillectomy is a common procedure, it still carries some possible risks, such as difficulty in swallowing, sore throat, and wound bleeding. In more severe cases, it can lead to significant bleeding, pleural effusion, pneumonia, and other complications. If any abnormalities are detected, it is recommended to seek medical attention immediately.
Here are some postoperative care guidelines to help speed up recovery:
- Refrain from forceful coughing within the first 24 hours post-surgery to avoid bleeding from the wound.
- Consume cold liquid foods within the first 24 hours after surgery, gradually returning to normal diet once the wound scabs have fallen off.
- Take a light diet for a week after surgery, avoiding hard, hot, acidic, rough, or spicy foods.
- Rinse the mouth with water after eating to maintain oral hygiene.
- Avoid vigorous exercise for the first four weeks after surgery.
- Take medications and attend follow-up appointments as directed by the doctor.
The ENT Centre at St. Paul's Hospital offers comprehensive professional ENT examination and treatment services, with experienced and patient-centered otolaryngologists and medical team responsible for diagnosis, treatment and postoperative care. For inquiry or consultation, please feel free to schedule a consultation appointment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is tonsillitis contagious?
Tonsillitis can be transmitted through respiratory droplets. When a patient coughs, sneezes, or even speaks, these viruses can spread into the air with the droplets. If inhaled, there is a high chance of infection, leading to tonsillitis.
What are some remedies for tonsillitis?
Ensuring adequate sleep helps the body repair itself, boosts the immune system, and fights off viral or bacterial infections; it's also important to keep the throat moist by drinking plenty of fluids. Additionally, gargling with salt water can help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation, alleviating sore throat symptoms. Keeping the air humid to prevent throat dryness can be achieved by using a humidifier or placing a bowl of water in the room. If symptoms worsen or discomfort persists, seek medical advice for a professional diagnosis and treatment.
How many days does tonsillitis usually last?
Generally, most patients will experience gradual symptom relief within 3 to 4 days. However, due to the variety of pathogens that can cause tonsillitis and individual differences in immune response and health status, some patients may have prolonged symptoms lasting up to 2 weeks or even experience recurrent episodes.
How many days should antibiotics for tonsillitis be taken?
Typically, antibiotics should be taken for 5 to 10 days to ensure the best therapeutic effect.
What can I eat to relieve tonsillitis?
If swallowing solid foods is difficult due to throat pain, liquid foods such as porridge, broth, or juice are good options. These foods are easy to swallow and will not irritate the throat. When the throat pain improves somewhat, you can try soft foods like steamed eggs, porridge, or noodles. These foods are easy to digest and provide the necessary nutrition for the body.
What dietary restrictions should be observed during tonsillitis?
During tonsillitis, avoid consuming excessively hot or cold, spicy, acidic, fried, barbecued, or greasy foods and stimulating beverages such as alcohol, caffeine as well as carbonated drinks.