.jpg)
Why do I have haemorrhoid (pile)?
Haemorrhoid are dilated veins around the anus. Aging, overweight, pregnancy, constipation, chronic diarrhoea, prolonged straining during defecation, lack of food fibre and prolonged sitting are the causes of haemorrhoids.
What are the symptoms?
Haemorrhoids can cause bleeding, pain, anal swelling and prolapse.
Does it hurt?
Haemorrhoids usually are painless. If haemorrhoids become thrombosed, it will lead to painful anal swelling, and even bleeding.
Anal pain can be due to other causes, e.g. anal fissure, perianal abscess, dermatitis and anal tumour. In order to find out the cause, assessment by a doctor is essential.
How many types of haemorrhoids are there?
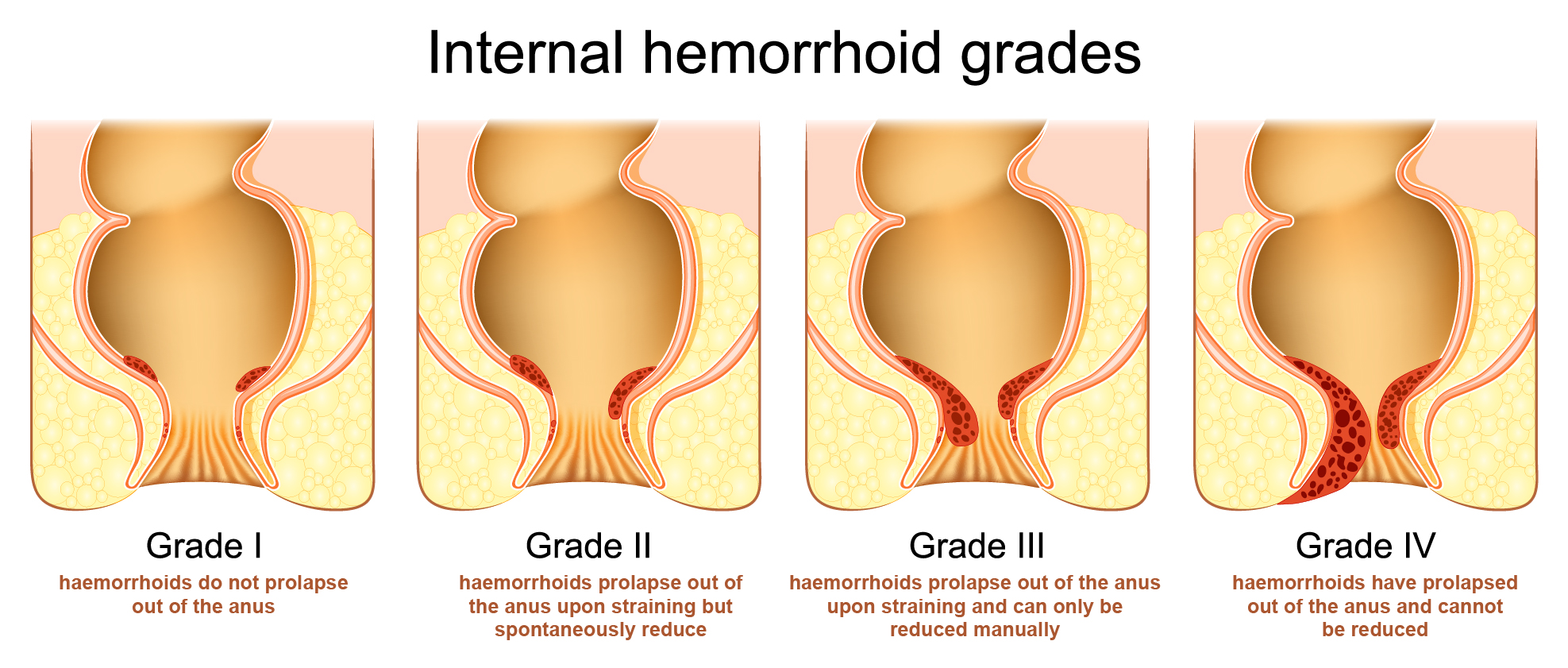
Haemorrhoids can be external, internal or mixed. Depending on the symptom and severity, internal haemorrhoids can be classified into four grades.
Grade I – haemorrhoids do not prolapse out of the anus.
Grade II – haemorrhoids prolapse out of the anus upon straining but spontaneously reduce.
Grade III – haemorrhoids prolapse out of the anus upon straining and can only be reduced manually.
Grade IV – haemorrhoids have prolapsed out of the anus and cannot be reduced.
How to treat it?
Treatment of haemorrhoids depends on the grading, severity, symptom and the needs of patients. Early and mild haemorrhoids can be relieved by conservative treatment, including diet and lifestyle modification, oral drug, topical ointment and suppository. If bleeding persists, rubber banding ligation of haemorrhoid can be an option. Rubber band ligation cuts off the blood supply of haemorrhoid, causing the haemorrhoid to shrink and drop off. If symptoms are severe or external haemorrhoids are troublesome, haemorrhoidectomy could be considered.
Haemorrhoid ligation can be performed at outpatient setting or at end of colonoscopy, and the procedure is simple and safe. After ligation, you will feel anal distention and the urge to defecate for three to four days. You may also experience mild pain and minor bleeding. The wound will be recovered within one to two
weeks.
How to prevent haemorrhoid?
Drink adequate water can improve constipation, which will in turn, prevent haemorrhoid formation.
Also, maintain a regular bowel habit, avoid prolonged sitting and pushing too hard during bowel opening, avoid alcohol and spicy food, eat more high-fiber food, control body weight, regular exercise and avoid sitting for long hours would help to prevent haemorrhoid.
Will sitting for long hours increase the chance of developing haemorrhoid?
Since sitting for long hours may increase the pressure on anal veins, it may increase the chance of developing haemorrhoid.
Will playing on mobile phone or reading while emptying bowel increase the chance of developing haemorrhoid?
Playing mobile phone or reading causes distraction of bowel emptying and prolongs sitting time on toilet. As a result, it increases the chance of haemorrhoid development.